Ribbon负载均衡原理
ribbon 是一个客户端负载均衡器,可以简单的理解成类似于 nginx的负载均衡模块的功能。
Load Balance负载均衡是用于解决一台机器(一个进程)无法解决所有请求而产生的一种算法。像nginx可以使用负载均衡分配流量,ribbon为客户端提供负载均衡,dubbo服务调用里的负载均衡等等,很多地方都使用到了负载均衡。
主流的Load Balance方案可分成两类:
一种是集中式Load Balance, 即在服务的消费方和提供方之间使用独立的LB设施(可以是硬件,如F5, 也可以是软件,如nginx), 由该设施负责把访问请求通过某种策略转发至服务的提供方;
另一种是进程内Load Balance,将LB逻辑集成到消费方,消费方从服务注册中心获知有哪些地址可用,然后自己再从这些地址中选择出一个合适的服务器。Ribbon就属于后者,它只是一个类库,集成于消费方进程,消费方通过它来获取到服务提供方的地址。
使用负载均衡带来的好处很明显:
当集群里的1台或者多台服务器down的时候,剩余的没有down的服务器可以保证服务的继续使用
使用了更多的机器保证了机器的良性使用,不会由于某一高峰时刻导致系统cpu急剧上升
负载均衡有好几种实现策略,常见的有:
- 随机 (Random)
- 轮询 (RoundRobin)
- 一致性哈希 (ConsistentHash)
- 哈希 (Hash)
- 加权(Weighted)
Ribbon的组成:
| 接口 | 作用 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| IClientConfig | 读取配置 | DefaultClientConfigImpl |
| IRule | 负载均衡规则,选择实例 | ZoneAvoidanceRule |
| IPing | 筛选掉ping不通的实例 | DummyPing |
| ServerList |
交给Ribbon的实例列表 | Ribbon:ConfigurationBasedServerList Spring Cloud Alibaba:NacosServerList |
| ServerListFilter |
过滤掉不符合条件的实例 | ZonePreferenceServerListFilter |
| ILoadBalance | Ribbon的入口 | ZoneAwareLoadBalance |
| ServerListUpdater | 更新交给Ribbon的List的策略 | PollingServerListUpdater |
Ribbon是比较灵活的,它对所有的组件都定义成了接口,如果对默认值不满意,可以实现这些接口配置一下,就可以将默认实现替换掉。
ILoadBalance 负载均衡器
ribbon是一个为客户端提供负载均衡功能的服务,它内部提供了一个叫做ILoadBalance的接口代表负载均衡器的操作,比如有添加服务器操作、选择服务器操作、获取所有的服务器列表、获取可用的服务器列表等等。
ILoadBalance的实现类如下:

image.png
负载均衡器是从服务发现组件(NacosDiscoveryClient或EurekaClient)(DiscoveryClient的实现类为NacosDiscoveryClient)获取服务信息,根据IRule去路由,并且根据IPing判断服务的可用性。
负载均衡器多久一次去获取一次从DiscoveryClient获取注册信息呢?在BaseLoadBalancer类下,BaseLoadBalancer的构造函数,该构造函数开启了一个PingTask任务setupPingTask();,代码如下:
public BaseLoadBalancer(String name, IRule rule, LoadBalancerStats stats, IPing ping, IPingStrategy pingStrategy) {
this.rule = DEFAULT_RULE;
this.pingStrategy = DEFAULT_PING_STRATEGY;
this.ping = null;
this.allServerList = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList());
this.upServerList = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList());
this.allServerLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
this.upServerLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
this.name = "default";
this.lbTimer = null;
this.pingIntervalSeconds = 10;
this.maxTotalPingTimeSeconds = 5;
this.serverComparator = new ServerComparator();
this.pingInProgress = new AtomicBoolean(false);
this.counter = Monitors.newCounter("LoadBalancer_ChooseServer");
this.enablePrimingConnections = false;
this.changeListeners = new CopyOnWriteArrayList();
this.serverStatusListeners = new CopyOnWriteArrayList();
logger.debug("LoadBalancer [{}]: initialized", name);
this.name = name;
this.ping = ping;
this.pingStrategy = pingStrategy;
this.setRule(rule);
this.setupPingTask();
this.lbStats = stats;
this.init();
}setupPingTask()的具体代码逻辑,它开启了ShutdownEnabledTimer执行PingTask任务,在默认情况下pingIntervalSeconds为10,即每10秒钟,向EurekaClient发送一次”ping”。
void setupPingTask() {
if (!this.canSkipPing()) {
if (this.lbTimer != null) {
this.lbTimer.cancel();
}
this.lbTimer = new ShutdownEnabledTimer("NFLoadBalancer-PingTimer-" + this.name, true);
this.lbTimer.schedule(new BaseLoadBalancer.PingTask(), 0L, (long)(this.pingIntervalSeconds * 1000));
this.forceQuickPing();
}
}PingTask源码,即new一个Pinger对象,并执行runPinger()方法。
查看Pinger的runPinger()方法,最终根据 pingerStrategy.pingServers(ping, allServers)来获取服务的可用性,如果该返回结果,如之前相同,则不去向EurekaClient获取注册列表,如果不同则通知ServerStatusChangeListener或者changeListeners发生了改变,进行更新或者重新拉取。
完整过程是:
LoadBalancerClient(RibbonLoadBalancerClient是实现类)在初始化的时候(execute方法),会通过ILoadBalance(BaseLoadBalancer是实现类)向Eureka注册中心获取服务注册列表,并且每10s一次向EurekaClient或NacosClient发送“ping”,来判断服务的可用性,如果服务的可用性发生了改变或者服务数量和之前的不一致,则从注册中心更新或者重新拉取。LoadBalancerClient有了这些服务注册列表,就可以根据具体的IRule来进行负载均衡。
IRule 路由
IRule接口代表负载均衡策略:
public interface IRule {
Server choose(Object var1);
void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer var1);
ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer();
}IRule接口的实现类有以下几种:
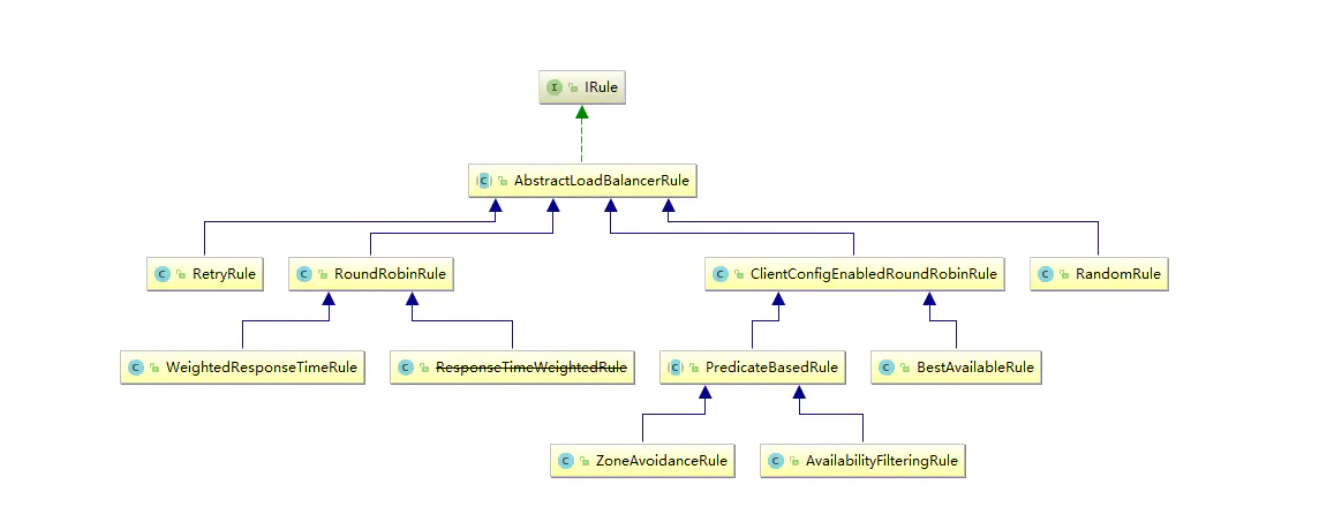
image.png
Ribbon内置的负载均衡规则:
| 规则名称 | 特点 |
|---|---|
| AvailabilityFilteringRule | 过滤掉一直连接失败的被标记为circuit tripped的后端Server,并 过滤掉那些高并发的后端Server或者使用一个AvailabilityPredicate 来包含过滤server的逻辑,其实就是检查status里记录的各个server 的运行状态 |
| BestAvailableRule | 选择一个最小的并发请求的server,逐个考察server, 如果Server被tripped了,则跳过 |
| RandomRule | 随机选择一个Server |
| ResponseTimeWeightedRule | 已废弃,作用同WeightedResponseTimeRule |
| WeightedResponseTimeRule | 根据响应时间加权,响应时间越长,权重越小,被选中的可能性越低 |
| RetryRule | 对选定的负载均衡策略加上重试机制,在一个配置时间段内当 选择Server不成功,则一直尝试使用subRule的方式选择一个 可用的Server |
| RoundRobinRule | 轮询选择,轮询index,选择index对应位置的Server |
| ZoneAvoidanceRule | 默认的负载均衡策略,即复合判断Server所在区域的性能和Server的可用性 选择Server,在没有区域的环境下,类似于轮询(RandomRule) |
其中RandomRule表示随机策略、RoundRobinRule表示轮询策略、WeightedResponseTimeRule表示加权策略、BestAvailableRule表示请求数最少策略等等。
随机策略很简单,就是从服务器中随机选择一个服务器,RandomRule的实现代码如下:
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {
if (lb == null) {
return null;
} else {
Server server = null;
while(server == null) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
return null;
}
List<Server> upList = lb.getReachableServers();
List<Server> allList = lb.getAllServers();
int serverCount = allList.size();
if (serverCount == 0) {
return null;
}
int index = this.chooseRandomInt(serverCount) ;//随机获取索引值index
server = (Server)upList.get(index); // 得到服务器实例
if (server == null) {
Thread.yield();
} else {
if (server.isAlive()) {
return server;
}
server = null;
Thread.yield();
}
}
return server;
}
}
protected int chooseRandomInt(int serverCount) {
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(serverCount);
}
public Server choose(Object key) {
return this.choose(this.getLoadBalancer(), key);
}RoundRobinRule轮询策略表示每次都取下一个服务器,比如一共有5台服务器,第1次取第1台,第2次取第2台,第3次取第3台,以此类推:
WeightedResponseTimeRule继承了RoundRobinRule,开始的时候还没有权重列表,采用父类的轮询方式,有一个默认每30秒更新一次权重列表的定时任务,该定时任务会根据实例的响应时间来更新权重列表,choose方法做的事情就是,用一个(0,1)的随机double数乘以最大的权重得到randomWeight,然后遍历权重列表,找出第一个比randomWeight大的实例下标,然后返回该实例,代码略。
BestAvailableRule策略用来选取最少并发量请求的服务器:
public Server choose(Object key) {
if (loadBalancerStats == null) {
return super.choose(key);
}
List<Server> serverList = getLoadBalancer().getAllServers();
int minimalConcurrentConnections = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Server chosen = null;
for (Server server: serverList) {
ServerStats serverStats = loadBalancerStats.getSingleServerStat(server);
if (!serverStats.isCircuitBreakerTripped(currentTime)) {
int concurrentConnections = serverStats.getActiveRequestsCount(currentTime);
if (concurrentConnections < minimalConcurrentConnections) {
minimalConcurrentConnections = concurrentConnections;
chosen = server;
}
}
}
if (chosen == null) {
return super.choose(key);
} else {
return chosen;
}
}使用Ribbon提供的负载均衡策略很简单,只需以下几部:
1、创建具有负载均衡功能的RestTemplate实例
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}使用RestTemplate进行rest操作的时候,会自动使用负载均衡策略,它内部会在RestTemplate中加入LoadBalancerInterceptor这个拦截器,这个拦截器的作用就是使用负载均衡。
默认情况下会采用轮询策略,如果希望采用其它策略,则指定IRule实现,如:
@Bean
public IRule ribbonRule() {
return new BestAvailableRule();
}这种方式对Feign也有效。
2、实现Ribbon细粒度的配置,即如果微服务order-center调用微服务user-center和微服务goods-center,order-center调用user-center使用随机,order-center调用goods-center使用默认ZoneAvoidanceRule
- Java代码配置
@Configuration
@RibbonClient(name="user-center",configuration = RibbonConfiguration.class)
public class UserCenterRibbonConfiguration {
}在SpringBoot启动类以外新建ribbonconfiguration包,并新建RibbonConfiguration类
/**
* @author: huangyibo
* @Date: 2019/11/2 18:08
* @Description: 如果将此类放进启动类的包下,那么此工程的所有ribbon都会使用这种负载均衡规则
*/
@Configuration
public class RibbonConfiguration {
//Ribbon提供的负载均衡策略
@Bean
public IRule ribbonRule(){
return new RandomRule();
}
}- 用配置属性配置
# 通过配置文件指定user-center实例的ribbon负载均衡策略为RandomRule,和java代码方式指定效果一样
user-center:
ribbon:
NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule-
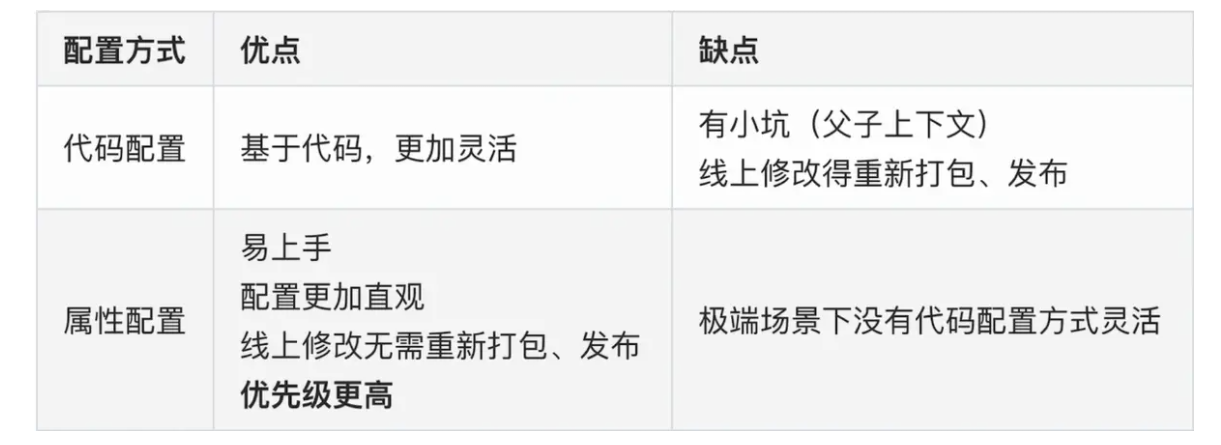
Ribbon细粒度配置最佳实践总结
代码配置方式 VS 属性配置方式
image.png
1)、尽量使用属性配置,属性方式实现不了的情况下再考虑使用代码配置
2)、在同一个微服务内尽量保持单一性,比如统一使用属性配置,不要两种方式混用,增加代码定位的复杂性
3、实现Ribbon的全局配置
@Configuration
@RibbonClients(defaultConfiguration = RibbonConfiguration.class)//Ribbon负载均衡的全局配置
public class UserCenterRibbonConfiguration {
}4、前面表格中的Ribbon的组成每一项都可以自定义,例如:
- Java代码配置
@Configuration
public class RibbonConfiguration {
//Ribbon提供的负载均衡策略
@Bean
public IRule ribbonRule(){
return new RandomRule();
}
@Bean
public IPing ping(){
return new PingUrl();
}
}- 用配置属性配置
clientName.ribbon.如下属性: - NFLoadBalancerClassName:ILoadBalancer实现类
- NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName:IRule实现类
- NFLoadBalancerPingClassName:IPing实现类
- NIWSServerListClassName:ServerList实现类
- NIWSServerListFilterClassName:ServerListFilter实现类
5、Ribbon的饥饿加载,Ribbon默认是懒加载的
ribbon:
eager-load:
# 开启ribbon饥饿加载
enabled: true
# 配置user-center使用ribbon饥饿加载,多个使用逗号分隔
clients: user-center6、扩展Ribbon,支持Nocas权重
-
编辑Nacos权重

新建NacosWeightedRule
/**
* @author: huangyibo
* @Date: 2019/11/2 18:44
* @Description: 继承AbstractLoadBalancerRule编写负载均衡算法,支持Nacos的权重
*/
@Slf4j
public class NacosWeightedRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule {
/**
* NacosDiscoveryProperties内置了基于权重的负载均衡算法
*/
@Autowired
private NacosDiscoveryProperties nacosDiscoveryProperties;
/**
* 读取配置文件并初始化NacosWeightedRule
* @param iClientConfig
*/
@Override
public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig iClientConfig) {
}
/**
* 实现基于权重的负载均衡算法
* @param o
*/
@Override
public Server choose(Object o) {
try {
BaseLoadBalancer loadBalancer = (BaseLoadBalancer)this.getLoadBalancer();
log.info("loadBalancer={}",loadBalancer);
//想要请求的微服务名称
String name = loadBalancer.getName();
//拿到服务发现新的相关的api
NamingService namingService = nacosDiscoveryProperties.namingServiceInstance();
//Nacos client自动通过基于权重的负载均衡算法,给我们选择一个实例
Instance instance = namingService.selectOneHealthyInstance(name);
log.info("Nacos client选择的实例:port={} , instance={}",instance.getPort(),instance);
return new NacosServer(instance);
} catch (NacosException e) {
log.error("Nacos client自动通过基于权重的负载均衡算法,选择微服务实例异常,e={}",e);
return null;
}
}
}
//spring cloud commons ---> 定义了标准
//spring cloud loadbalancer --->定义了各种负载均衡器的标准 没有权重配置NacosWeightedRule
@Configuration
public class RibbonConfiguration {
//自定义负载均衡配置,通过Nacos client自动通过基于权重的负载均衡算法,给我们选择一个实例
@Bean
public IRule ribbonRule(){
return new NacosWeightedRule();
}
}
@Configuration
@RibbonClients(defaultConfiguration = RibbonConfiguration.class)//Ribbon负载均衡的全局配置
public class UserCenterRibbonConfiguration {
}7、扩展Ribbon,实现Nacos注册中心同一集群优先调用
新建NacosSameClusterWeightedRule
/**
* @author: huangyibo
* @Date: 2019/11/2 19:03
* @Description: 继承AbstractLoadBalancerRule拓展Ribbon,进行同一集群下服务优先调用,这个是针对的异地灾备的
*/
@Slf4j
public class NacosSameClusterWeightedRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule {
@Autowired
private NacosDiscoveryProperties nacosDiscoveryProperties;
@Override
public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig iClientConfig) {
}
@Override
public Server choose(Object o) {
try {
//拿到配置文件中的集群名称 shenzhen
String clusterName = nacosDiscoveryProperties.getClusterName();
BaseLoadBalancer loadBalancer = (BaseLoadBalancer)this.getLoadBalancer();
log.info("loadBalancer={}",loadBalancer);
//想要请求的微服务名称
String name = loadBalancer.getName();
//拿到服务发现新的相关的api
NamingService namingService = nacosDiscoveryProperties.namingServiceInstance();
//1、找到指定服务的所有实例 A
List<Instance> instances = namingService.selectInstances(name, true);
//instances.get(0).getMetadata();//获取实例的元数据
//2、过滤出相同集群下的所有实例 B
List<Instance> sameClustInstances = instances.stream()
.filter(instance -> Objects.equals(instance.getClusterName(), clusterName))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
//3、如果B是空,就用A
List<Instance> instancesToBeChosen = new ArrayList<>();
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sameClustInstances)){
instancesToBeChosen = instances;
log.warn("发生跨集群的调用,name={},clusterName={},instances={}",name,clusterName,instances);
}else {
instancesToBeChosen = sameClustInstances;
}
//4、基于权重的负载均衡算法,返回1个实例
Instance instance = ExtendBalancer.getHostByRandomWeight2(instancesToBeChosen);
log.info("选择的实例是:port={},instance={}",instance.getPort(),instance);
return new NacosServer(instance);
} catch (NacosException e) {
log.error("发生异常了,e={}",e);
return null;
}
}
}
//当Balancer类下面的getHostByRandomWeight方法不能直接调用的时候,继承它然后去调用
class ExtendBalancer extends Balancer{
public static Instance getHostByRandomWeight2(List<Instance> hosts) {
return getHostByRandomWeight(hosts);
}
}配置application.yml
spring:
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: localhost:8848
cluster-name: shanghai配置NacosSameClusterWeightedRule
@Configuration
public class RibbonConfiguration {
//自定义负载均衡配置,通过Nacos client拓展Ribbon,进行同一集群下服务优先调用,这个是针对的异地灾备的
@Bean
public IRule ribbonRule(){
return new NacosSameClusterWeightedRule();
}
}8、扩展Ribbon,实现Nacos注册中心基于元数据的版本控制
Nacos元数据的配置:
spring:
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: localhost:8848
cluster-name: shanghai
metadata:
# 自己这个实例的版本
version: V1
# 允许调用的提供者版本
target-version: V1新建NacosRule实现AbstractLoadBalancerRule
@Slf4j
public class NacosRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule {
@Autowired
private NacosDiscoveryProperties nacosDiscoveryProperties;
@Override
public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig iClientConfig) {
}
@Override
public Server choose(Object o) {
try {
//负载均衡规则:优先调用同一集群下,符合metadata元数据的实例
//如果没有,就选择所有集群下,符合metadata的实例
//1、查询所有实例 A
//2、筛选元数据匹配的实例 B
//3、筛选出同cluster下元数据匹配的实例 C
//4、如果C为空,就用B
//5、随机选择实例
String clusterName = nacosDiscoveryProperties.getClusterName();
String targerVersion = nacosDiscoveryProperties.getMetadata().get("target-version");
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer loadBalancer = (DynamicServerListLoadBalancer)this.getLoadBalancer();
//想要请求的微服务名称
String name = loadBalancer.getName();
//拿到服务发现新的相关的api
NamingService namingService = nacosDiscoveryProperties.namingServiceInstance();
//所有实例
List<Instance> instances = namingService.selectInstances(name, true);
List<Instance> metadataMatchInstances = new ArrayList<>();
//如果配置了版本映射,那么只调用元数据匹配的实例
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(targerVersion)){
metadataMatchInstances = instances.stream()
.filter(instance -> Objects.equals(targerVersion,instance.getMetadata().get("target-version")))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(metadataMatchInstances)){
log.warn("未找到元数据匹配的目标实例!请检查配置,目标元数据配置为:targerVersion={}",targerVersion);
return null;
}
}
List<Instance> clusterMetadataMatchInstances = new ArrayList<>();
//如果配置了集群名称,需筛选同集群下元数据匹配的实例
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(clusterName)){
clusterMetadataMatchInstances = metadataMatchInstances.stream()
.filter(instance -> Objects.equals(clusterName,instance.getClusterName()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(clusterMetadataMatchInstances)){
clusterMetadataMatchInstances = metadataMatchInstances;
log.warn("发生跨集群的调用,name={},clusterName={},targerVersion={},instances={}",name,clusterName,targerVersion,instances);
}
}
Instance instance = ExtendBalancer.getHostByRandomWeight2(clusterMetadataMatchInstances);
log.info("选择的实例是:port={},instance={}",instance.getPort(),instance);
return new NacosServer(instance);
} catch (NacosException e) {
log.error("发生异常了,e={}",e);
return null;
}
}
}负载均衡算法:
public class ExtendBalancer extends Balancer {
/**
* 根据权重,随机选择实例
*
* @param instances 实例列表
* @return 选择的实例
*/
public static Instance getHostByRandomWeight2(List<Instance> instances) {
return getHostByRandomWeight(instances);
}
}