explain关键字可以模拟MySQL优化器执行SQL语句,可以很好的分析SQL语句或表结构的性能瓶颈。
explain包含的字段
- id //select查询的序列号,包含一组数字,表示查询中执行select子句或操作表的顺序
- select_type //查询类型
- table //正在访问哪个表
- partitions //匹配的分区
- type //访问的类型
- possible_keys //显示可能应用在这张表中的索引,一个或多个,但不一定实际使用到
- key //实际使用到的索引,如果为NULL,则没有使用索引
- key_len //表示索引中使用的字节数,可通过该列计算查询中使用的索引的长度
- ref //显示索引的哪一列被使用了,如果可能的话,是一个常数,哪些列或常量被用于查找索引列上的值
- rows //根据表统计信息及索引选用情况,大致估算出找到所需的记录所需读取的行数
- filtered //查询的表行占表的百分比
- Extra //包
数据准备
create table subject(
id int(10) auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
teacher_id int(10),
primary key (id),
index idx_teacher_id (teacher_id)
);//学科表
create table teacher(
id int(10) auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
teacher_no varchar(20),
primary key (id),
unique index unx_teacher_no (teacher_no(20))
);//教师表
create table student(
id int(10) auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
student_no varchar(20),
primary key (id),
unique index unx_student_no (student_no(20))
);//学生表
create table student_score(
id int(10) auto_increment,
student_id int(10),
subject_id int(10),
score int(10),
primary key (id),
index idx_student_id (student_id),
index idx_subject_id (subject_id)
);//学生成绩表
alter table teacher add index idx_name(name(20)); //教师表增加名字普通索引
数据填充:
insert into student(name,student_no) values ('zhangsan','20200001'),('lisi','20200002'),('yan','20200003'),('dede','20200004');
insert into teacher(name,teacher_no) values('wangsi','T2010001'),('sunsi','T2010002'),('jiangsi','T2010003'),('zhousi','T2010004');
insert into subject(name,teacher_id) values('math',1),('Chinese',2),('English',3),('history',4);
insert into student_score(student_id,subject_id,score) values(1,1,90),(1,2,60),(1,3,80),(1,4,100),(2,4,60),(2,3,50),(2,2,80),(2,1,90),(3,1,90),(3,4,100),(4,1,40),(4,2,80),(4,3,80),(4,5,100);explain 分析
分析几个重点字段
id
1. id相同
执行顺序从上至下
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject,student_score,teacher where subject.id = student_id and subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;读取顺序:subject > teacher > student_score
2. id不同
如果是子查询,id的序号会递增,id的值越大优先级越高,越先被执行
例子:
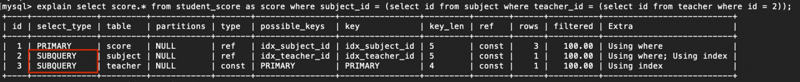
explain select score.* from student_score as score where subject_id = (select id from subject where teacher_id = (select id from teacher where id = 2));读取顺序:teacher > subject > student_score
3. id相同又不同
id如果相同,可以认为是一组,从上往下顺序执行。在所有组中,id值越大,优先级越高,越先执行
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject left join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id
union
select subject.* from subject right join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;读取顺序:2.teacher > 2.subject > 1.subject > 1.teacher
select_type
- simple:表示不需要union操作或者不包含子查询的简单select查询。有连接查询时,外层的查询为simple,且只有一个
- primary:一个需要union操作或者含有子查询的select,位于最外层的单位查询的select_type即为primary。且只有一个
- union:union连接的两个select查询,第一个查询是dervied派生表,除了第一个表外,第二个以后的表select_type都是union
- dependent union:与union一样,出现在union 或union all语句中,但是这个查询要受到外部查询的影响
- union result:包含union的结果集,在union和union all语句中,因为它不需要参与查询,所以id字段为null
- subquery:除了from字句中包含的子查询外,其他地方出现的子查询都可能是subquery
- dependent subquery:与dependent union类似,表示这个subquery的查询要受到外部表查询的影响
- derived:from字句中出现的子查询,也叫做派生表,其他数据库中可能叫做内联视图或嵌套select
SIMPLE
简单查询,不包含子查询或Union查询
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject,student_score,teacher where subject.id = student_id and subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;PRIMARY
查询中若包含任何复杂的子部分,最外层查询则被标记为主查询
例子:
explain select score.* from student_score as score where subject_id = (select id from subject where teacher_id = (select id from teacher where id = 2));SUBQUERY
在select或where中包含子查询
例子:
explain select score.* from student_score as score where subject_id = (select id from subject where teacher_id = (select id from teacher where id = 2));DERIVED
在FROM列表中包含的子查询被标记为DERIVED(衍生),MySQL会递归执行这些子查询,把结果放在临时表中 备注: MySQL5.7+ 进行优化了,增加了derived_merge(派生合并),默认开启,可加快查询效率
UNION
若第二个select出现在uion之后,则被标记为UNION
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject left join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id
union
select subject.* from subject right join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;UNION RESULT
从UNION表获取结果的select
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject left join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id
union
select subject.* from subject right join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;type
- system:表中只有一行数据或者是空表,且只能用于myisam和memory表。如果是Innodb引擎表,type列在这个情况通常都是all或者index
- const:使用唯一索引或者主键,返回记录一定是1行记录的等值where条件时,通常type是const。其他数据库也叫做唯一索引扫描
- eq_ref:出现在要连接过个表的查询计划中,驱动表只返回一行数据,且这行数据是第二个表的主键或者唯一索引,且必须为not null,唯一索引和主键是多列时,只有所有的列都用作比较时才会出现eq_ref
- ref:不像eq_ref那样要求连接顺序,也没有主键和唯一索引的要求,只要使用相等条件检索时就可能出现,常见与辅助索引的等值查找。或者多列主键、唯一索引中,使用第一个列之外的列作为等值查找也会出现,总之,返回数据不唯一的等值查找就可能出现。
- fulltext:全文索引检索,要注意,全文索引的优先级很高,若全文索引和普通索引同时存在时,mysql不管代价,优先选择使用全文索引
- ref_or_null:与ref方法类似,只是增加了null值的比较。实际用的不多。
- unique_subquery:用于where中的in形式子查询,子查询返回不重复值唯一值
- index_subquery:用于in形式子查询使用到了辅助索引或者in常数列表,子查询可能返回重复值,可以使用索引将子查询去重。
- range:索引范围扫描,常见于使用>,<,is null,between ,in ,like等运算符的查询中。
- index_merge:表示查询使用了两个以上的索引,最后取交集或者并集,常见and ,or的条件使用了不同的索引,官方排序这个在ref_or_null之后,但是实际上由于要读取所个索引,性能可能大部分时间都不如range
- index:索引全表扫描,把索引从头到尾扫一遍,常见于使用索引列就可以处理不需要读取数据文件的查询、可以使用索引排序或者分组的查询。
- all:这个就是全表扫描数据文件,然后再在server层进行过滤返回符合要求的记录。
NULL > system > const > eq_ref > ref > fulltext > ref_or_null > index_merge > unique_subquery > index_subquery > range > index > ALL //最好到最差
- NULL
MySQL能够在优化阶段分解查询语句,在执行阶段用不着再访问表或索引
例子:
explain select min(id) from subject;- system
表只有一行记录(等于系统表),这是const类型的特列,平时不大会出现,可以忽略
- const
表示通过索引一次就找到了,const用于比较primary key或uique索引,因为只匹配一行数据,所以很快,如主键置于where列表中,MySQL就能将该查询转换为一个常量
例子:
explain select * from teacher where teacher_no = 'T2010001';- eq_ref
唯一性索引扫描,对于每个索引键,表中只有一条记录与之匹配,常见于主键或唯一索引扫描
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject left join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;- ref
非唯一性索引扫描,返回匹配某个单独值的所有行 本质上也是一种索引访问,返回所有匹配某个单独值的行 然而可能会找到多个符合条件的行,应该属于查找和扫描的混合体
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject,student_score,teacher where subject.id = student_id and subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;- ref_or_null
类似ref,但是可以搜索值为NULL的行
例子:
explain select * from teacher where name = 'wangsi' or name is null;- index_merge
表示使用了索引合并的优化方法
例子:
explain select * from teacher where id = 1 or teacher_no = 'T2010001'- range
只检索给定范围的行,使用一个索引来选择行,key列显示使用了哪个索引 一般就是在你的where语句中出现between、<>、in等的查询。
例子:
explain select * from subject where id between 1 and 3;- index
Full index Scan,Index与All区别:index只遍历索引树,通常比All快 因为索引文件通常比数据文件小,也就是虽然all和index都是读全表,但index是从索引中读取的,而all是从硬盘读的。
例子:
explain select id from subject;- ALL
Full Table Scan,将遍历全表以找到匹配行
例子:
explain select * from subject;key_len
表示查询优化器使用了索引的字节数. 这个字段可以评估组合索引是否完全被使用, 或只有最左部分字段被使用到.
key_len 的计算规则如下:
- 字符串
- char(n): n 字节长度
- varchar(n): 如果是 utf8 编码, 则是 3 n + 2字节; 如果是 utf8mb4 编码, 则是 4 n + 2 字节.
- 数值类型:
- TINYINT: 1字节
- SMALLINT: 2字节
- MEDIUMINT: 3字节
- INT: 4字节
- BIGINT: 8字节
- 时间类型
- DATE: 3字节
- TIMESTAMP: 4字节
- DATETIME: 8字节
字段属性: NULL 属性 占用一个字节. 如果一个字段是 NOT NULL 的, 则没有此属性.
rows
rows 也是一个重要的字段. MySQL 查询优化器根据统计信息, 估算 SQL 要查找到结果集需要扫描读取的数据行数. 这个值非常直观显示 SQL 的效率好坏, 原则上 rows 越少越好.
extra
EXplain 中的很多额外的信息会在 Extra 字段显示, 常见的有以下几种内容:
- distinct:在select部分使用了distinc关键字
- no tables used:不带from字句的查询或者From dual查询
- 使用not in()形式子查询或not exists运算符的连接查询,这种叫做反连接。即,一般连接查询是先查询内表,再查询外表,反连接就是先查询外表,再查询内表。
- using filesort:排序时无法使用到索引时,就会出现这个。常见于order by和group by语句中
- using index:查询时不需要回表查询,直接通过索引就可以获取查询的数据。
- using join buffer(block nested loop),using join buffer(batched key accss):5.6.x之后的版本优化关联查询的BNL,BKA特性。主要是减少内表的循环数量以及比较顺序地扫描查询。
- using sort_union,using_union,using intersect,using sort_intersection:
- using intersect:表示使用and的各个索引的条件时,该信息表示是从处理结果获取交集
- using union:表示使用or连接各个使用索引的条件时,该信息表示从处理结果获取并集
- using sort_union和using sort_intersection:与前面两个对应的类似,只是他们是出现在用and和or查询信息量大时,先查询主键,然后进行排序合并后,才能读取记录并返回。
- using temporary:表示使用了临时表存储中间结果。临时表可以是内存临时表和磁盘临时表,执行计划中看不出来,需要查看status变量,used_tmp_table,used_tmp_disk_table才能看出来。
- using where:表示存储引擎返回的记录并不是所有的都满足查询条件,需要在server层进行过滤。查询条件中分为限制条件和检查条件,5.6之前,存储引擎只能根据限制条件扫描数据并返回,然后server层根据检查条件进行过滤再返回真正符合查询的数据。5.6.x之后支持ICP特性,可以把检查条件也下推到存储引擎层,不符合检查条件和限制条件的数据,直接不读取,这样就大大减少了存储引擎扫描的记录数量。extra列显示using index condition
- firstmatch(tb_name):5.6.x开始引入的优化子查询的新特性之一,常见于where字句含有in()类型的子查询。如果内表的数据量比较大,就可能出现这个
- loosescan(m..n):5.6.x之后引入的优化子查询的新特性之一,在in()类型的子查询中,子查询返回的可能有重复记录时,就可能出现这个
- Using filesort
说明MySQL会对数据使用一个外部的索引排序,而不是按照表内的索引顺序进行读取 MySQL中无法利用索引完成的排序操作称为“文件排序”
例子:
explain select * from subject order by name;- Using temporary
使用了临时表保存中间结果,MySQL在对结果排序时使用临时表,常见于排序order by 和分组查询group by
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject left join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id
union
select subject.* from subject right join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;- Using index
表示相应的select操作中使用了覆盖索引(Covering Index),避免访问了表的数据行,效率不错! 如果同时出现using where,表明索引被用来执行索引键值的查找 如果没有同时出现using where,表明索引用来读取数据而非执行查找动作
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject,student_score,teacher where subject.id = student_id and subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;
备注: 覆盖索引:select的数据列只用从索引中就能够取得,不必读取数据行,MySQL可以利用索引返回select列表中的字段,而不必根据索引再次读取数据文件,即查询列要被所建的索引覆盖
- Using where
使用了where条件
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject,student_score,teacher where subject.id = student_id and subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;- Using join buffer
使用了连接缓存
例子:
explain select student.*,teacher.*,subject.* from student,teacher,subject;- impossible where
where子句的值总是false,不能用来获取任何元组
例子:
explain select * from teacher where name = 'wangsi' and name = 'lisi';- distinct
一旦mysql找到了与行相联合匹配的行,就不再搜索了
例子:
explain select distinct teacher.name from teacher left join subject on teacher.id = subject.teacher_id;- Select tables optimized away
SELECT操作已经优化到不能再优化了(MySQL根本没有遍历表或索引就返回数据了)
例子:
explain select min(id) from subject;